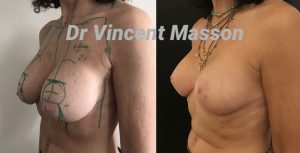
Breast ptosis, empty and sagging breasts
What is the definition of breast ptosis?
Breast ptosis is defined as sagging or drooping breasts. The breast volume itself may be normal, too small (hypotrophic or emptied breasts) or too large (hypertrophic breasts). The degree of breast sagging can be described using a ptosis scale: grade 1 (mild ptosis), the areola is above the fold under the breast; grade 2 (moderate ptosis), the areola is level with the fold under the breast or slightly below; grades 3 and 4 (advanced ptosis), the areola is clearly below the fold under the breast and points downwards.
Sagging breasts are treated by various cosmetic surgery procedures, with or without visible scars, depending on the case and the degree of ptosis.

What are the causes of breast ptosis?
The most frequent causes are:
- Congenital, the breast has had the appearance of sagging from adolescence. The breast has a normal size or, on the contrary, can be too small (hypotrophy), emptied or too large (hypertrophy).
- Pregnancy, breastfeeding and hormonal reasons are very frequent causes: weight gain and loss, lactation, breast volume development during pregnancy, hormonal imbalances, and prolonged breastfeeding can contribute to the onset of breast ptosis.
- Weight variations: variations in weight and massive weight loss weaken the skin, ligaments, and all the anatomical structures that support the breast and can lead to breast ptosis with a sagging and emptied breast.
- Skin aging, sagging skin, and loss of skin elasticity over the years.
What are the possible treatments ?
Many breast ptosis correction techniques are possible and should be established on a case by case basis:
- According to the patient’s wishes.
- The degree of ptosis (grades 1 to 4).
- Breast shape.
- Breast volume.
- Skin quality.
We always start first by solving the volume problem.
If the breast has a normal volume and is suitable for the patient, the volume is not touched and the breast is simply lifted.
If the breast is too large, it will have to be reduced by removing the excess breast tissue.
If the breast is too small or completely emptied as is often the case, it is then essential to add volume, either by means of, most usually, breast implants or by performing a fat transfer or lipofilling (fat liposuction from one part of the body and reinjection into the breast) provided that the breast does not sag too much.
The next step is to perform the ptosis correction itself, the breast lift, also known as a mastopexy.
It is during this stage that the excess skin will be removed, the shape of the breast formed and the breast reassembled.
Different scars are possible depending on the degree of breast ptosis. The goal is to avoid scarring as much as possible.
In some cases, a scar under the areola (areolar route) or under the breast hidden in the shadow of the submammary groove and very short (submammary route), associated with the placement of an implant in dual plane is sufficient to correct moderate ptosis.
In other cases, an incision is made around the areola (periareolar incision), known as the round block technique. This technique makes it possible to slightly raise the breast and to reconcentrate or reduce an overly large areola. This is a technique that was used a great deal a few years ago but less and less now. The risks of this technique are that it can cause puckering around the areola, a large scar, and a recurrence of the enlargement of the areola several years later. This technique is reserved for moderate ptosis.
Finally in the cases of more significant ptosis (the majority of cases), it is necessary to make an incision around the areola associated with a vertical scar (vertical technique), which goes from the areola to the submammary groove. The idea of this scar often frightens patients but you should know that in a rather paradoxical way, compared to what you might think, it is very discreet and often almost invisible. Finally, in certain cases of significant ptosis it is essential to carry out, in addition to the vertical scar and the one around the areola, a submammary scar which will be hidden in the groove (a T-shaped scar).
What should you do before a breast ptosis procedure?
Have a consultation with the cosmetic surgeon.
Take a blood test.
Have a consultation with the clinic’s anesthetist.
A mammography and/or ultrasound in some cases.
Buy a specific type of compression bra.
Stop smoking as soon as possible (ameliorates wound healing).
Do not take aspirin (it causes bleeding).
Plan to take one week off work after the operation.
Dr. Masson’s office is the very first in Paris to be equipped with 4D Eve 4.0 scanner technology.
When you come for a breast augmentation consultation you will be able to use augmented reality to discover how your new breasts will look.
What are the postoperative effects?
It all depends on the operation that is performed, but the following is worth noting:
- There is moderate breast pain for the first week, which is relieved by painkillers.
- Breast bandages are needed every day for a week.
- A compression bra has to be worn for one month.
- No sport or swimming is allowed for three weeks.
- One week off work is necessary.
How much does a ptosis correction cost? Information on prices.
The final price for a ptosis correction varies greatly because the procedures are very different from each other. The price depends on the type of scar, whether implants are fitted or not, the use of any lipofilling, the clinic costs, and the duration of the operation. In general, the costs range from 4,800 euros without implants and 7,500 euros with implants for the simplest cases to 9,000 euros for the most complex cases. As it is a cosmetic surgery treatment it is therefore normally not reimbursed by the health insurance systems. Sometimes treatment can be authorized in the event of an associated malformation or breast enlargement with more than 300 grams per breast to be removed, but in the vast majority of cases there is no health insurance support.